 打开微信扫一扫
打开微信扫一扫
复制链接














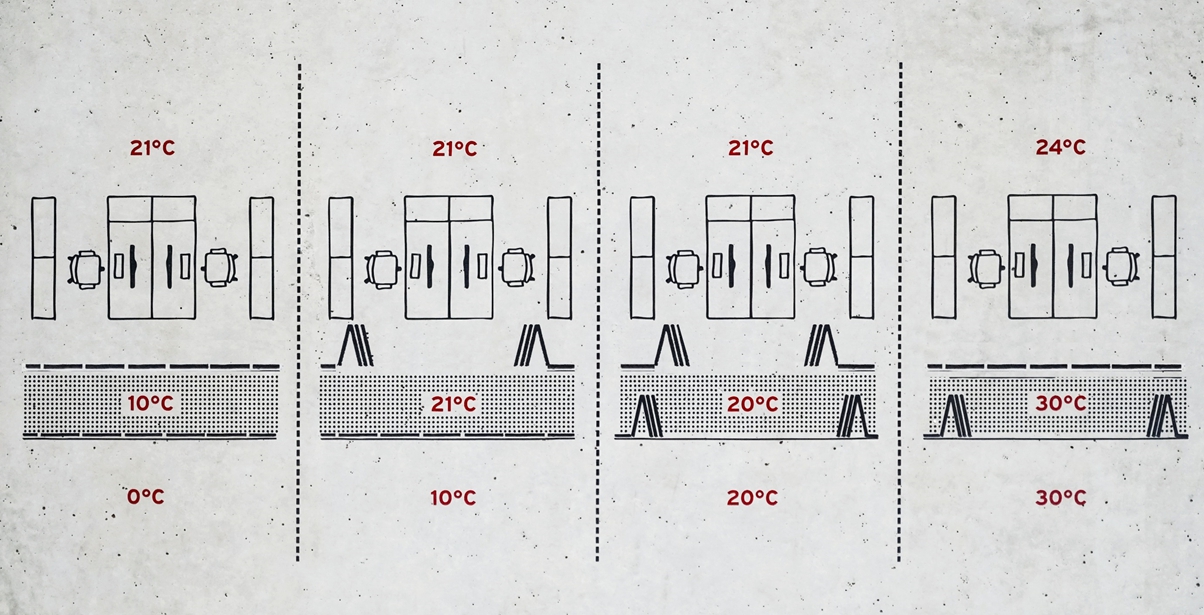
查看更多
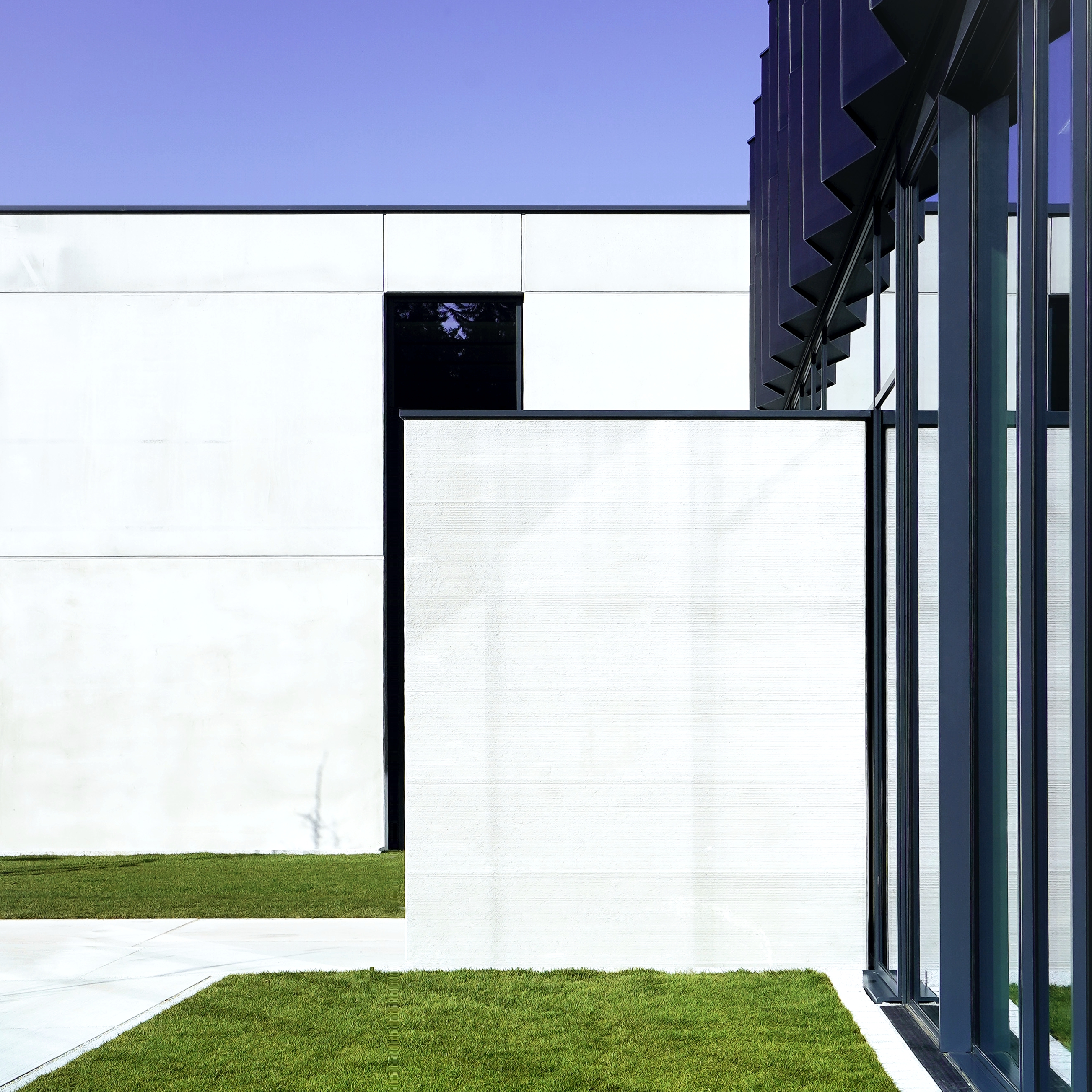
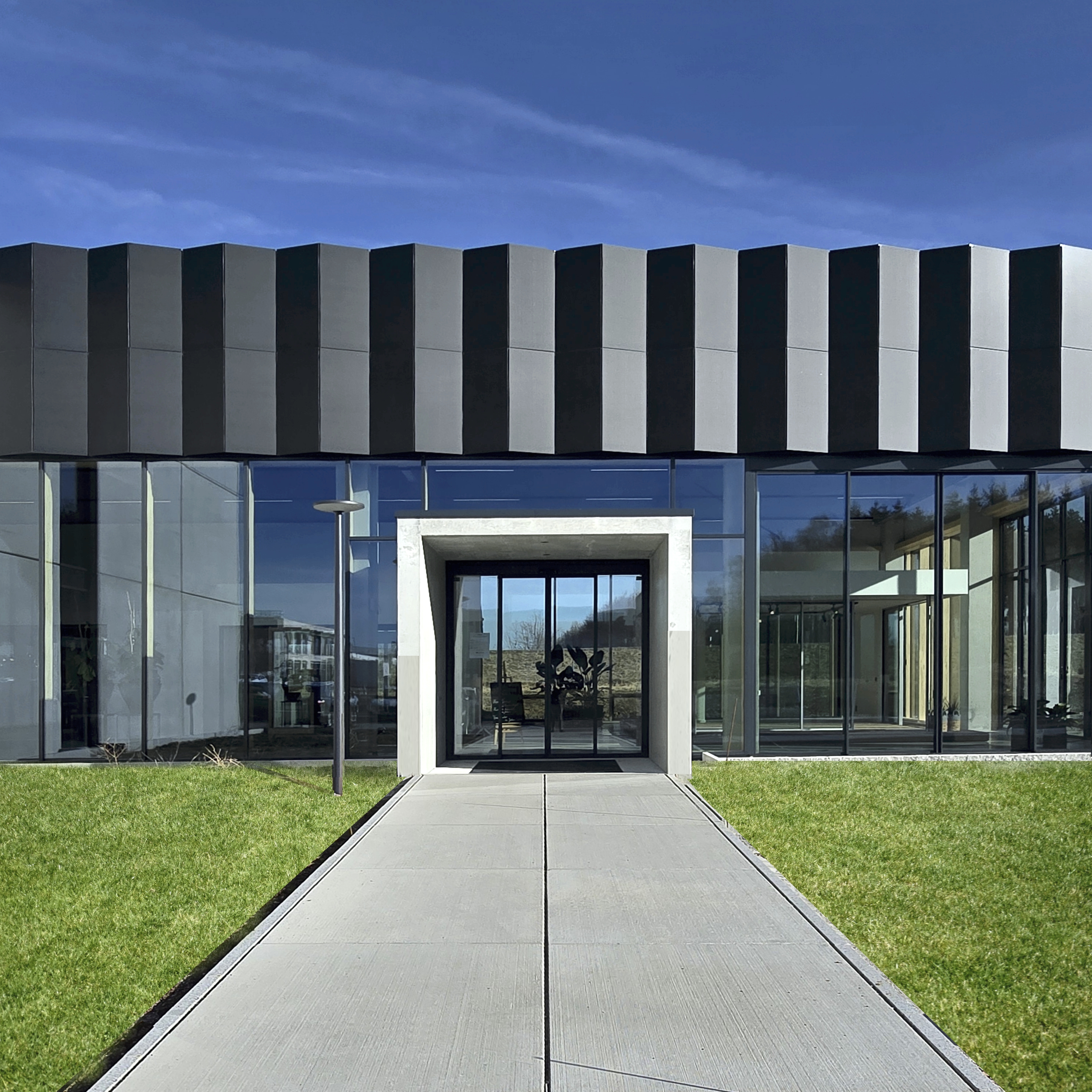
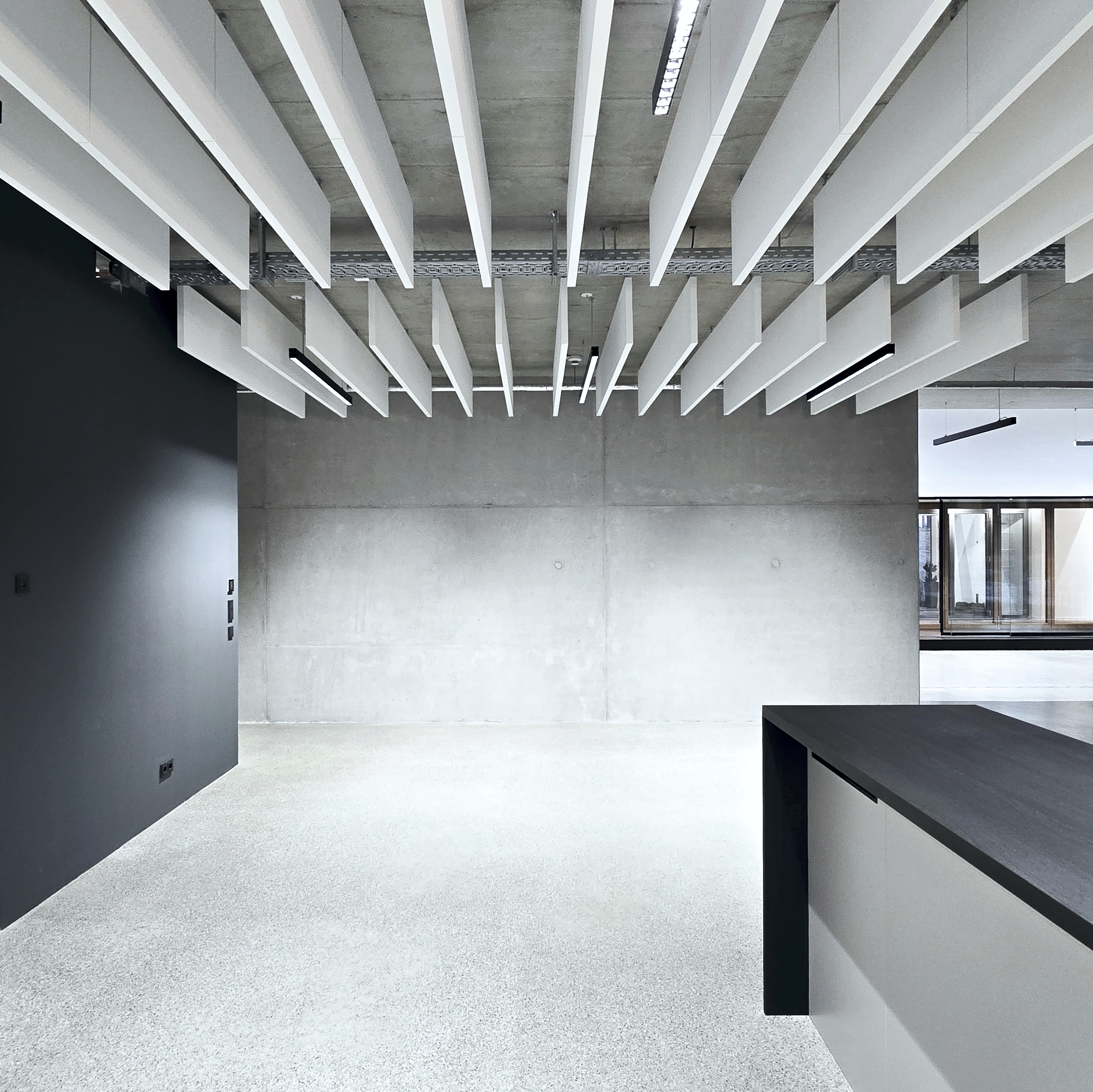
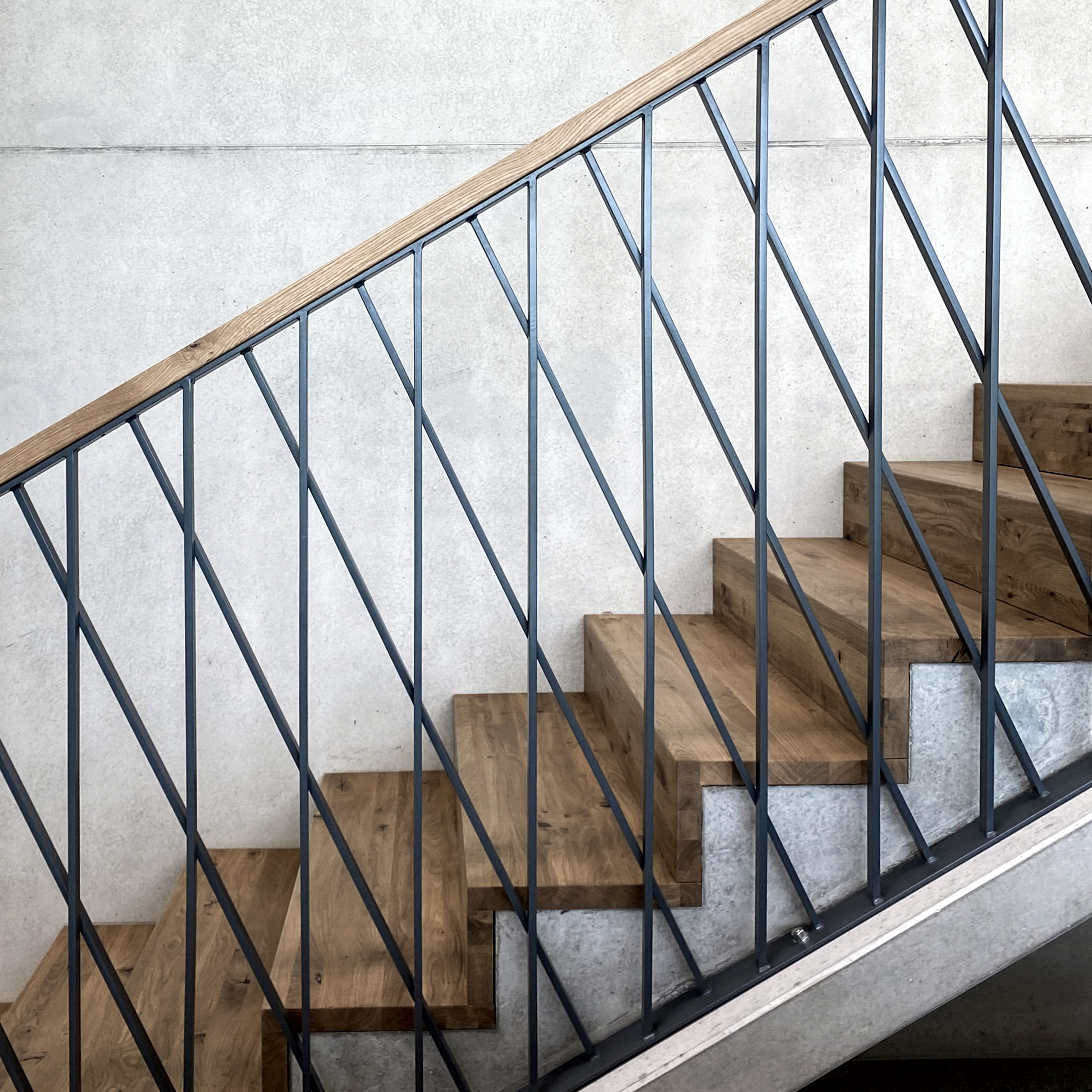
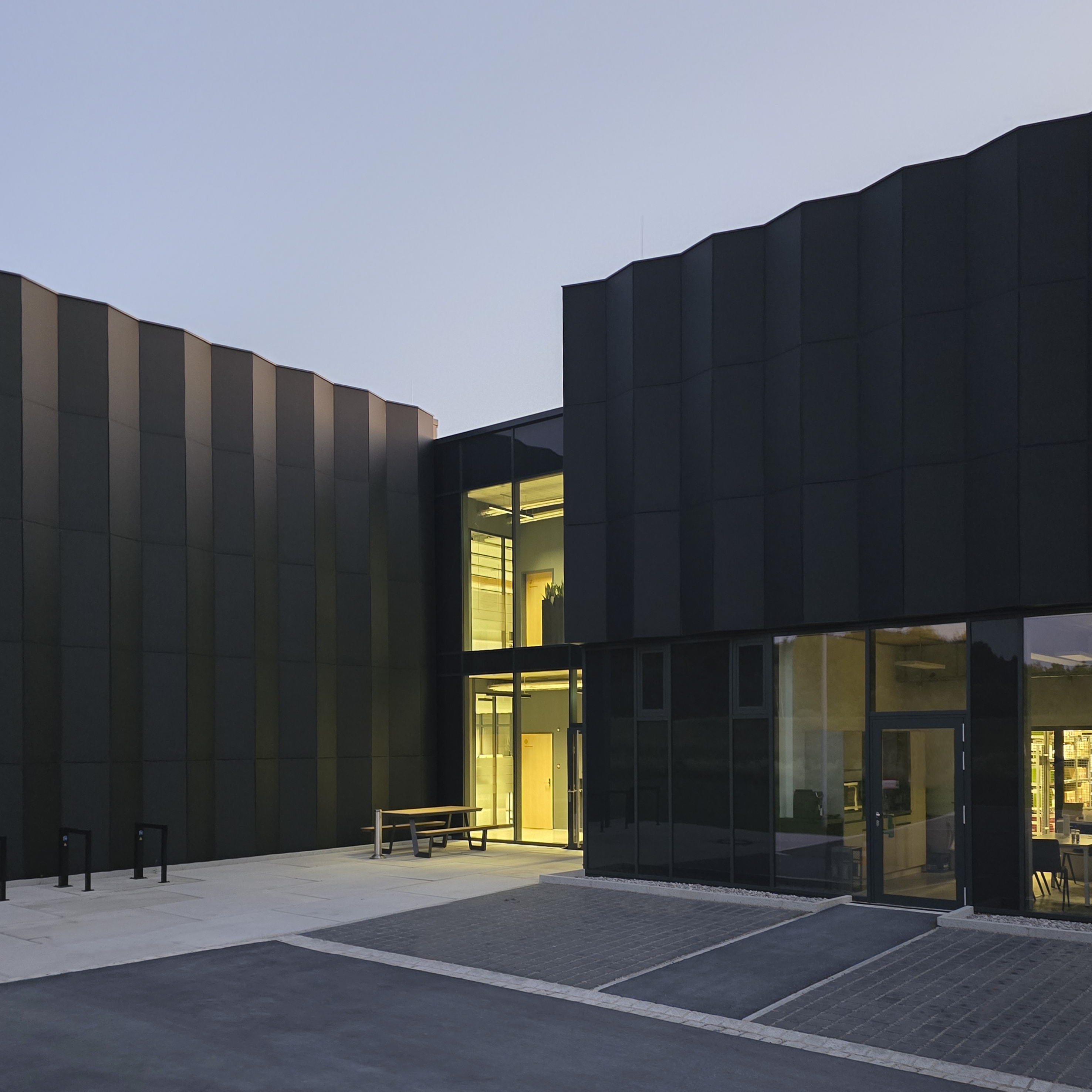
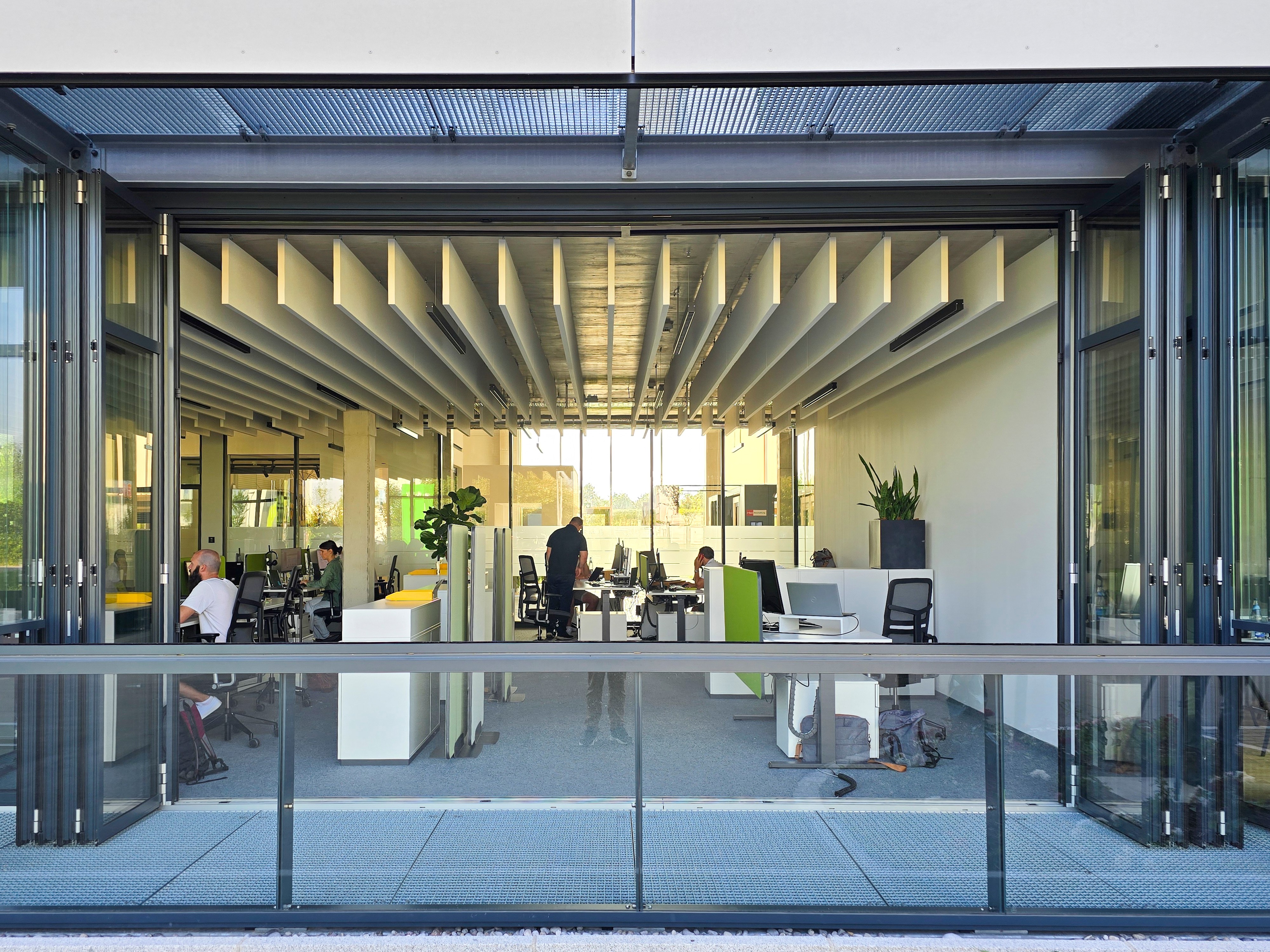
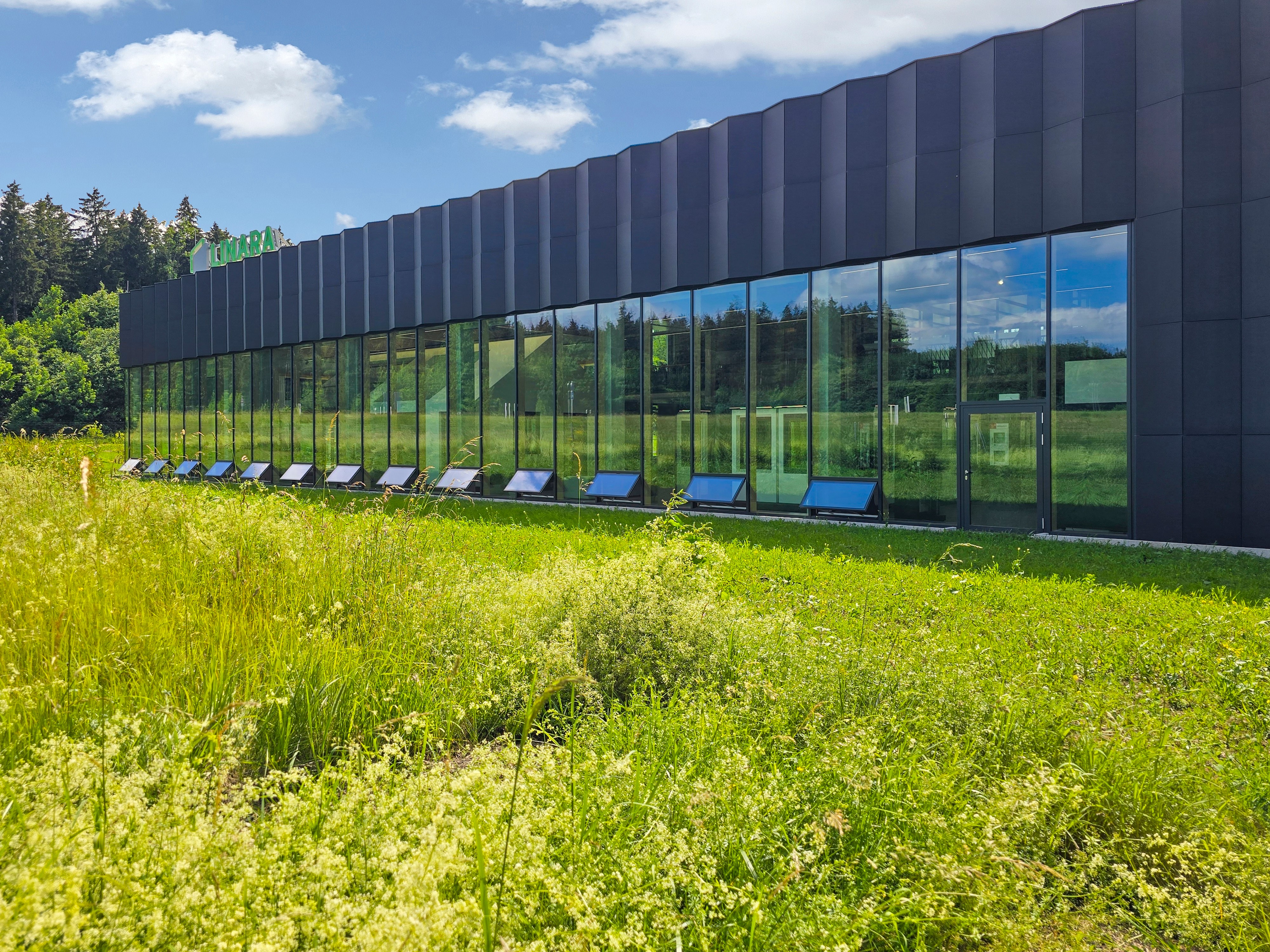
获奖者:Peter Kuczia | KUCZIA architects


